You may have heard of CryptoPunks and Bored Apes. They’re NFT series of 10,000 unique and randomly generated images of characters. They’re also 2 of the most well-known examples of ‘NFT avatars’ – a trend which has exploded in the crypto space of 2021 and is set to permeate subcultures once they move into the web3.
Here’s how, and why.
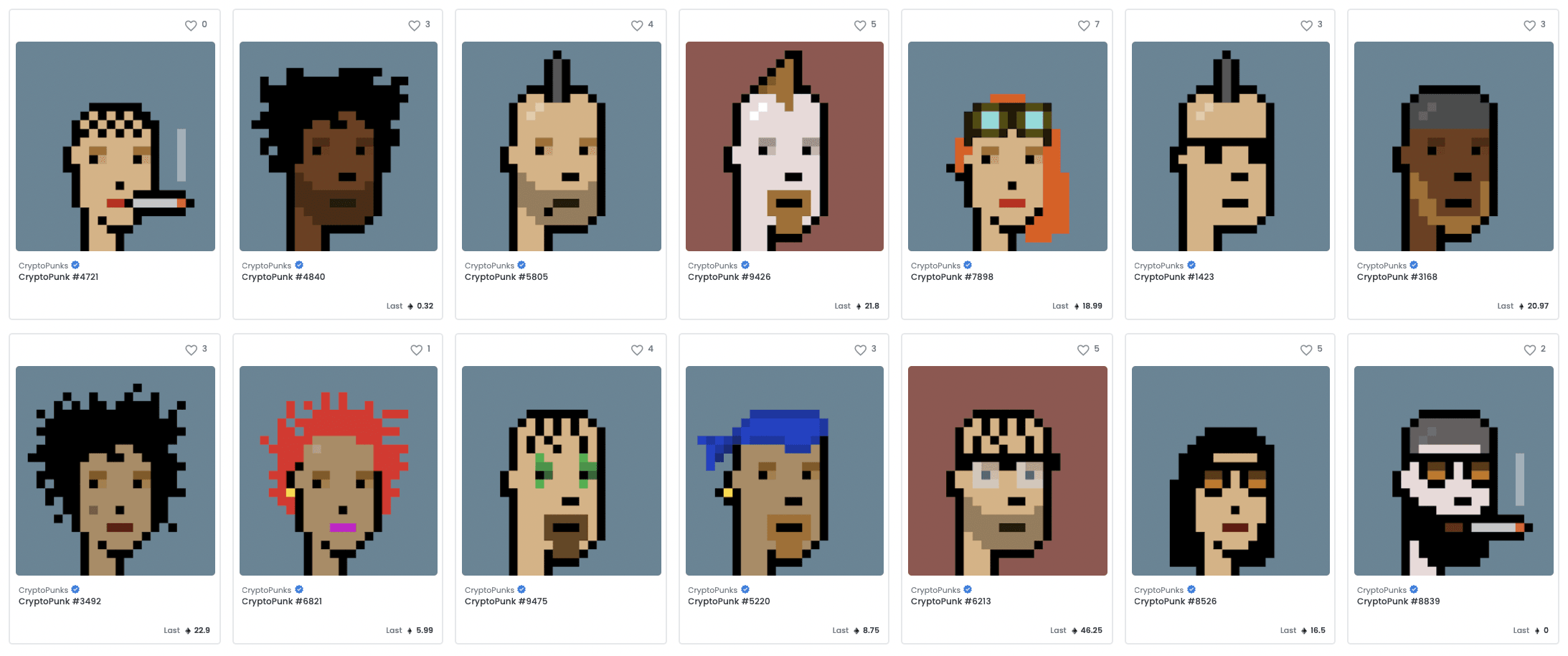
PFPs & NFT Avatars
NFT avatar projects are casually referred to as PFPs: ProFile Pictures, since that’s a common use case for them. They most often have up to 10,000 template characters that are ‘minted’ by people wanting to own one. Minting costs money (cryptocurrency) and in the process of minting randomized traits are applied, ranging from extremely rare to common. These may be variables like skin colour, headwear, haircuts, shirts, background colours and anything else you may think of that’s appropriate to the project. Many projects will have 10 traits with 10 variables per trait.
Once minted, the character is created and will remain unchanged, so before you mint, you usually only know what the style of the project is, but not what your NFT character will end up looking like. Once all NFTs from a series have been minted, the value of some of the PFPs may increase, since people may try to purchase ones that specifically appeal to them (like Jay-Z’s CryptoPunk).
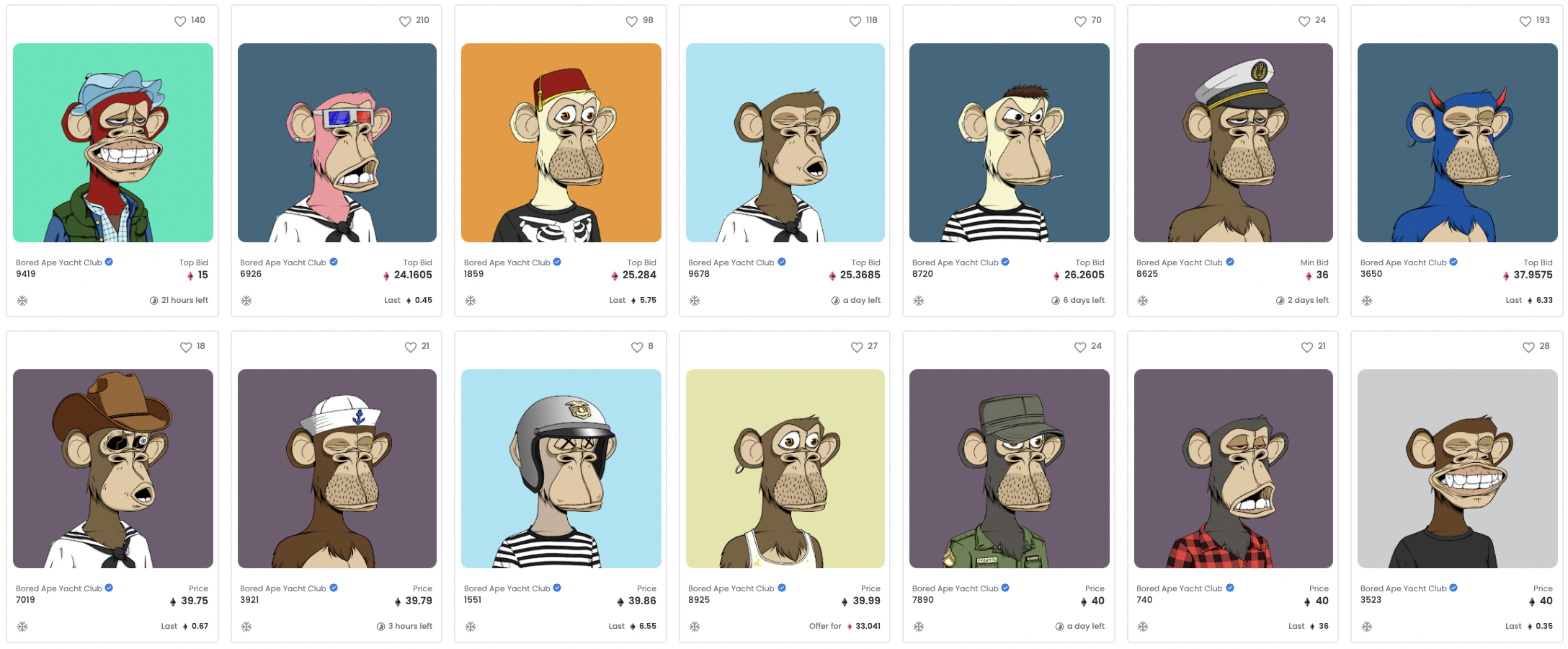
Being early
The creative web3 space is still relatively small. Many of the more successful projects specifically cater to the crypto community and its aesthetics. As interest has peaked, so have the number of PFP projects that now flood the space. Many struggle to get all their NFTs minted, often resulting in minted NFTs being sold for a price lower than the minting cost, which further slows down the minting process.
Yet we’re early. Many types of aesthetics that are popular in subcultures, for example as album artwork, in music videos, or as tattoos, don’t necessarily resonate well with those already onboarded to the web3. While some of the aesthetics emerging from the web3 space will go on to become cornerstones of emerging subcultures, a more diverse variety of aesthetics will become popular in the web3 as more people get onboarded.
A PFP project making slow progress on minting seems bad, but if it finds ways to onboard the subculture in which its aesthetics are rooted, it can succeed over time and enjoy a potentially more meaningful success than it could by shilling to speculating crypto bros (f/m/non-binary).
Onboarding subcultures
The social dynamics of what’s happening right now are not unique. The clearest memory I have of subcultures shifting to a new type of internet is from around 2009 when artists started switching out the MySpace Music players on their profiles for SoundCloud embeds. SoundCloud’s player was clearly superior. While MySpace limited you to a maximum number of tracks per profile, SoundCloud allowed you to upload 4 tracks of any length per month for free in those days. The benefits were obvious and thus once a few musicians in a genre embedded the SoundCloud player on their MySpace profile, you’d see it spread like wildfire through their subgenre.
The type of people who were the first to switch out their player, the innovators, are now onboarding to the web3. Many of them are already experimenting with NFTs and DAOs. PFPs allow them to signal the web3 to others in their cultural space, just like how the SoundCloud player signalled a shift from the age of downloads to the age of streaming. PFPs are not enough though, since their utility is not as obvious compared to an embeddable player that was easily twice as good as what preceded it.
For subcultures to onboard to the web3, there are two main hurdles to overcome:
- Proof of stake (PoS). The energy use associated with Proof of Work blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum has made many people unwilling to touch any type of crypto. So, I expect a few factors in the next year will drive more people to the web3: 1) Ethereum switching to PoS; 2) maturing ecosystems around PoS blockchains such as Tezos and Solana; 3) more accessible layer 2 rollups for more diverse use cases.
- Usability. It currently takes about 30-60 minutes to onboard someone to the web3 and buy their first NFT, like an ENS domain (see my primer below). They have to open a wallet, verify their identity on an exchange, buy crypto, wait for transactions to clear, etc. It’s hard to figure things out. It’s easy to make expensive mistakes. Many people who are already onboarded forget how hard it is: try onboarding a friend who’s completely new to it. Sit next to them. Walk them through all the steps.
Subcultures and PFPs
A year from now, things will likely be a lot easier for newcomers. Besides work being done on the previous two bullet points, tech giants like PayPal, Square / Cash App, and likely Facebook / Instagram entering the space will help decrease the number of hurdles (at the cost of decentralization).
It will increase the viability of sounds and images that are specific only to certain subcultures and decrease the necessity to make plays that cater to the wider web3 community. So if you’ve been hesitating to start a PFP project or a DAO, because you don’t think the people are onboard for it yet: start small and do it anyway. Consider a lower number than 10,000, and don’t rush, don’t shill too hard. Your audience will get here eventually and you’ll be the CryptoPunk equivalent of your domain. The OG PFP NFTs of your subculture.
I don’t know about you, but I’m so ready for crypto goth, crypto gabber, and actual crypto punk. See you soon.
